React Native Setup
This tutorial will guide you through integrating the iOS bindings and Android bindings into an React Native) project. Before you begin, make sure you’ve completed the "Getting Started - 3. Mopro build" process with selecting iOS platform and Android platform and have the MoproiOSBindings and MoproAndroidBindings folder ready:
React Native is a JavaScript framework that enables developers to build native apps for multiple platforms with a single codebase.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to create a native Mopro module on both Android and iOS simulators/devices.
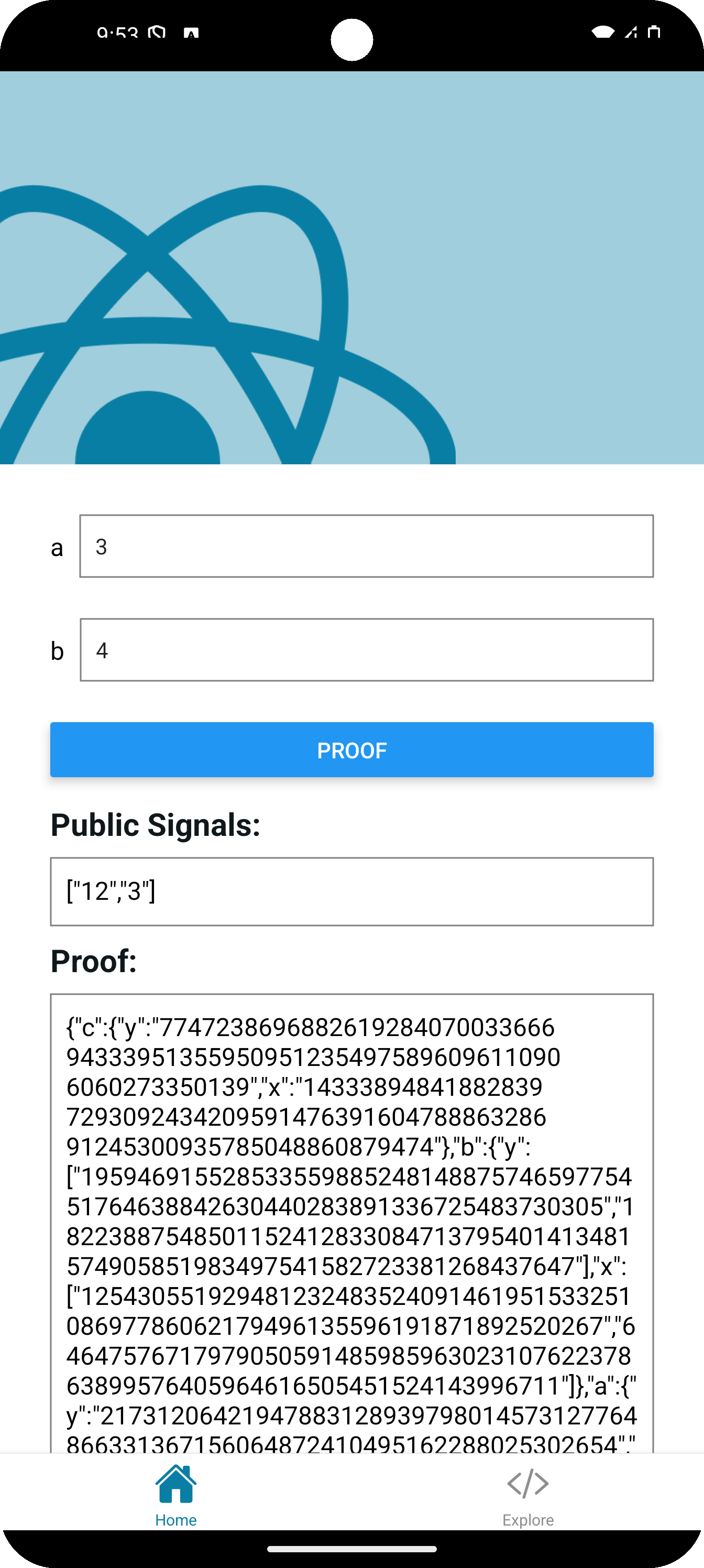
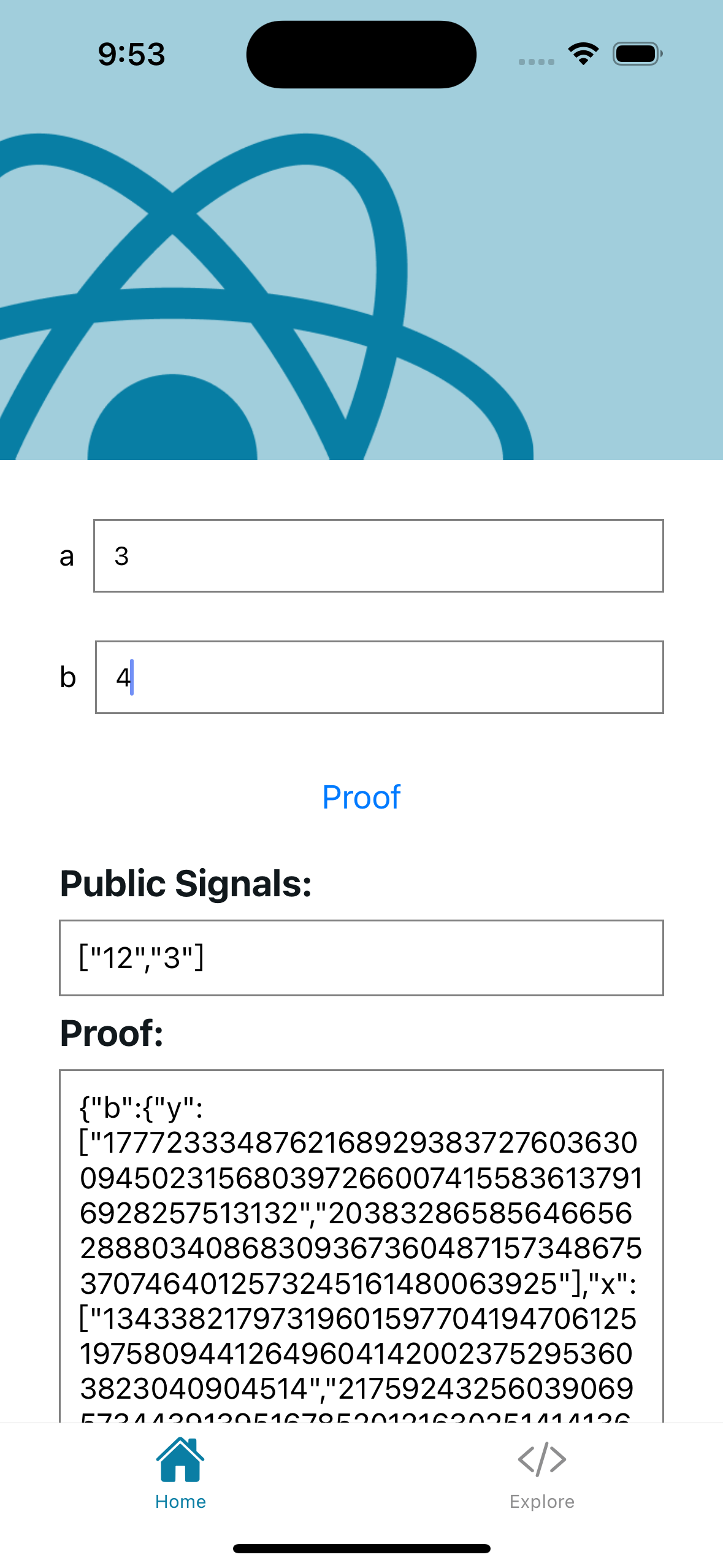
In this example, we use Circom circuits and their corresponding .zkey files. The process is similar for other provers.
0. Initialize an React Native project
First let's create a new React Native project. If you already have a React Native project you can skip this step.
-
Getting started with React Native: Official documentation
infoThe Expo framework is recommended by the React Native community. (Last updated on Apr 14, 2025)
We will use the Expo framework throughout this documentation.
Ref: Start a new React Native project with Expo -
After creating a React Native project, you should be able to run with a commands like
npm run iosfor iOS simulators. And
npm run androidfor Android emulators.
1. Creating a Native Module
-
Creating a native module by the command
npx create-expo-module --local moproIt will create a native module named
moproin themodules/moprofolder with the structure like this├── modules
│ └── mopro
│ ├── android
│ ├── expo-module.config.json
│ ├── index.ts
│ ├── ios
│ └── src
2. Implement the module on iOS
Please refer to react-native-app to see the latest update.
2-1 Use a framework
-
Get the
MoproiOSBindingsfrommopro build.infoSee Getting Started
-
Copy the
MoproiOSBindingsdirectory tomodules/mopro/ios -
Bundle the bindings in
Mopro.podspec/modules/mopro/ios/Mopro.podspec...
s.dependency 'ExpoModulesCore'
s.vendored_frameworks = 'MoproiOSBindings/MoproBindings.xcframework'
...
2-2 Create convertible types for Javascript library with swift.
-
Create a new file called
MoproType.swiftin the following folder:modules/mopro/iosFull
/modules/mopro/ios/MoproType.swift/modules/mopro/ios/MoproType.swiftimport ExpoModulesCore
struct ExpoG1: Record {
@Field
var x: String?
@Field
var y: String?
@Field
var z: String?
}
struct ExpoG2: Record {
@Field
var x: [String]?
@Field
var y: [String]?
@Field
var z: [String]?
}
struct ExpoProof: Record {
@Field
var a: ExpoG1?
@Field
var b: ExpoG2?
@Field
var c: ExpoG1?
@Field
var `protocol`: String?
@Field
var curve: String?
}
struct ExpoCircomProofResult: Record {
@Field
var inputs: [String]?
@Field
var proof: ExpoProof?
}
enum ProofLibOption: Int, Enumerable {
case arkworks
case rapidsnark
}
struct ExpoCircomProofLib: Record {
@Field
var proofLib: ProofLibOption = .arkworks
}
2-3. Create native module implementation in MoproModule.swift
-
Define helper functions to bridge types between the Mopro bindings and the Expo framework:
/modules/mopro/ios/MoproModule.swifthelpers/modules/mopro/ios/MoproModule.swiftimport ExpoModulesCore
import moproFFI
// convert the mopro proofs to be exposed to Expo framework
func convertCircomProof(proof: CircomProof) -> ExpoProof {
let a = ExpoG1()
a.x = proof.a.x
a.y = proof.a.y
a.z = proof.a.z
let b = ExpoG2()
b.x = proof.b.x
b.y = proof.b.y
b.z = proof.b.z
let c = ExpoG1()
c.x = proof.c.x
c.y = proof.c.y
c.z = proof.c.z
let expoProof = ExpoProof()
expoProof.a = a
expoProof.b = b
expoProof.c = c
expoProof.protocol = proof.protocol
expoProof.curve = proof.curve
return expoProof
}
// convert the Expo proofs to be used in mopro bindings
func convertCircomProofResult(proofResult: ExpoCircomProofResult) -> CircomProofResult {
guard let proof = proofResult.proof,
let a = proof.a,
let b = proof.b,
let c = proof.c,
let inputs = proofResult.inputs,
let `protocol` = proof.protocol,
let curve = proof.curve
else {
fatalError("Invalid proof result")
}
let g1a = G1(x: a.x ?? "0", y: a.y ?? "0", z: a.z ?? "1")
let g2b = G2(x: b.x ?? ["1", "0"], y: b.y ?? ["1", "0"], z: b.z ?? ["1", "0"])
let g1c = G1(x: c.x ?? "0", y: c.y ?? "0", z: c.z ?? "1")
let circomProof = CircomProof(
a: g1a, b: g2b, c: g1c, protocol: `protocol`, curve: curve)
let circomProofResult = CircomProofResult(proof: circomProof, inputs: inputs)
return circomProofResult
}
enum CircomError: Error {
case circomProofGenerationFailed(String)
case circomProofVerificationFailed(String)
} -
Define the native module API. See the Module API Reference for details.
modules/mopro/ios/MoproModule.swiftpublic class MoproModule: Module {
// Each module class must implement the definition function. The definition consists of components
// that describes the module's functionality and behavior.
// See https://docs.expo.dev/modules/module-api for more details about available components.
public func definition() -> ModuleDefinition {
// Sets the name of the module that JavaScript code will use to refer to the module. Takes a string as an argument.
// Can be inferred from module's class name, but it's recommended to set it explicitly for clarity.
// The module will be accessible from `requireNativeModule('Mopro')` in JavaScript.
Name("Mopro")
// ...
AsyncFunction("generateCircomProof") {
(zkeyPath: String, circuitInputs: String, expoProofLib: ExpoCircomProofLib) -> ExpoCircomProofResult in
do {
let proofLib = expoProofLib.proofLib == ProofLibOption.arkworks ? ProofLib.arkworks : ProofLib.rapidsnark
let res = try generateCircomProof(
zkeyPath: zkeyPath, circuitInputs: circuitInputs, proofLib: proofLib)
let result = ExpoCircomProofResult()
result.inputs = res.inputs
result.proof = convertCircomProof(proof: res.proof)
return result
} catch {
throw CircomError.circomProofGenerationFailed(error.localizedDescription)
}
}
AsyncFunction("verifyCircomProof") {
(zkeyPath: String, proofResult: ExpoCircomProofResult, proofLib: ExpoCircomProofLib) -> Bool in
do {
let proofLib = proofLib.proofLib == .arkworks ? ProofLib.arkworks : ProofLib.rapidsnark
let isValid = try verifyCircomProof(
zkeyPath: zkeyPath,
proofResult: convertCircomProofResult(proofResult: proofResult),
proofLib: ProofLib.arkworks
)
return isValid
} catch {
throw CircomError.circomProofVerificationFailed(error.localizedDescription)
}
}
// ...
}
3. Implement the module on Android
Please refer to react-native-app to see the latest update.
3-1. Add dependency for jna in the file build.gradle.
dependencies {
implementation("net.java.dev.jna:jna:5.13.0@aar")
}
3-2. Include Mopro bindings in the native Android module
- Get the
MoproAndroidBindingsfrommopro build.infoSee Getting Started
- Move the
jniLibsdirectory tomodules/mopro/android/src/main/.
And moveuniffidirectory tomodules/mopro/android/src/main/java/.
The folder structure should be as follows:modules/mopro/android/src/main
├── AndroidManifest.xml
├── assets
├── java
│ ├── expo
│ │ └── modules
│ │ └── mopro
│ │ ├── MoproModule.kt
│ │ └── MoproView.kt
��│ └── uniffi
│ └── mopro
│ └── mopro.kt
└── jniLibs
├── arm64-v8a
├── armeabi-v7a
├── x86
└── x86_64
3-3. Create convertible types for Javascript library with kotlin.
It is a better way to represent a JavaScript object with the native type safety.
-
Create a new file called
MoproType.ktin the following folder:modules/mopro/android/src/main/java/expo/modules/mopro/Full
/modules/mopro/android/src/main/java/expo/modules/mopro/MoproType.ktmodules/mopro/android/src/main/java/expo/modules/mopro/MoproType.ktpackage expo.modules.mopro
import expo.modules.kotlin.records.Field
import expo.modules.kotlin.records.Record
import expo.modules.kotlin.types.Enumerable
class ExpoG1 : Record {
@Field var x: String?
@Field var y: String?
@Field var z: String?
constructor(_x: String, _y: String, _z: String) {
x = _x
y = _y
z = _z
}
}
class ExpoG2 : Record {
@Field var x: List<String>?
@Field var y: List<String>?
@Field var z: List<String>?
constructor(_x: List<String>, _y: List<String>, _z: List<String>) {
x = _x
y = _y
z = _z
}
}
class ExpoProof : Record {
@Field var a: ExpoG1?
@Field var b: ExpoG2?
@Field var c: ExpoG1?
@Field var `protocol`: String?
@Field var curve: String?
constructor(_a: ExpoG1, _b: ExpoG2, _c: ExpoG1, _protocol: String, _curve: String) {
a = _a
b = _b
c = _c
`protocol` = _protocol
curve = _curve
}
}
class ExpoCircomProofResult : Record {
@Field var proof: ExpoProof?
@Field var inputs: List<String>?
constructor(_proof: ExpoProof, _inputs: List<String>) {
proof = _proof
inputs = _inputs
}
}
enum class ProofLibOption(val value: Int) : Enumerable {
arkworks(0),
rapidsnark(1)
}
class ExpoCircomProofLib : Record {
@Field
val proofLib: ProofLibOption = ProofLibOption.arkworks
}infoRef: Records
3-4. Create native module implementation in MoproModule.kt
-
Define helper functions to bridge types between the Mopro bindings and the Expo framework:
/modules/mopro/android/src/main/java/expo/modules/mopro/MoproModule.kthelpers/modules/mopro/android/src/main/java/expo/modules/mopro/MoproModule.kt// convert the mopro proofs to be exposed to Expo framework
fun convertCircomProof(proof: CircomProof): ExpoProof {
var a = ExpoG1(proof.a.x, proof.a.y, proof.a.z)
var b = ExpoG2(proof.b.x, proof.b.y, proof.b.z)
var c = ExpoG1(proof.c.x, proof.c.y, proof.c.z)
var output = ExpoProof(a, b, c, proof.protocol, proof.curve)
return output
}
// convert the Expo proofs to be used in mopro bindings
fun convertCircomProofResult(proofResult: ExpoCircomProofResult): CircomProofResult {
var g1a = G1(proofResult.proof?.a?.x ?: "0", proofResult.proof?.a?.y ?: "0", proofResult.proof?.a?.z ?: "1")
var g2b = G2(proofResult.proof?.b?.x ?: listOf("1", "0"), proofResult.proof?.b?.y ?: listOf("1", "0"), proofResult.proof?.b?.z ?: listOf("1", "0"))
var g1c = G1(proofResult.proof?.c?.x ?: "0", proofResult.proof?.c?.y ?: "0", proofResult.proof?.c?.z ?: "1")
var circomProof = CircomProof(g1a, g2b, g1c, proofResult.proof?.protocol ?: "groth16", proofResult.proof?.curve ?: "bn128")
var circomProofResult = CircomProofResult(circomProof, proofResult.inputs ?: listOf("0"))
return circomProofResult
} -
Define the native module API. See the Module API Reference for details.
modules/mopro/android/src/main/java/expo/modules/mopro/MoproModule.ktclass MoproModule : Module() {
// Each module class must implement the definition function. The definition consists of components
// that describes the module's functionality and behavior.
// See https://docs.expo.dev/modules/module-api for more details about available components.
override fun definition() = ModuleDefinition {
// Sets the name of the module that JavaScript code will use to refer to the module. Takes a string as an argument.
// Can be inferred from module's class name, but it's recommended to set it explicitly for clarity.
// The module will be accessible from `requireNativeModule('Mopro')` in JavaScript.
Name("Mopro")
// ...
AsyncFunction("generateCircomProof") { zkeyPath: String, circuitInputs: String, expoProofLib: ExpoCircomProofLib ->
try {
val file = File(zkeyPath)
if (!file.exists()) {
throw CodedException("ZkeyFileNotFound", "The zkey file was not found at path: $zkeyPath", null)
}
val proofLib = if (expoProofLib.proofLib == ProofLibOption.arkworks) ProofLib.ARKWORKS else ProofLib.RAPIDSNARK
val res = generateCircomProof(file.absolutePath, circuitInputs, proofLib)
ExpoCircomProofResult(convertCircomProof(res.proof), res.inputs)
} catch (e: Exception) {
throw CodedException("GenerateProofFailed", "Unknown error occurred during proof generation", e)
}
}
AsyncFunction("verifyCircomProof") { zkeyPath: String, proofResult: ExpoCircomProofResult, expoProofLib: ExpoCircomProofLib ->
try {
val file = File(zkeyPath)
if (!file.exists()) {
throw CodedException("ZkeyFileNotFound", "The zkey file was not found at path: $zkeyPath", null)
}
val proofLib = if (expoProofLib.proofLib == ProofLibOption.arkworks) ProofLib.ARKWORKS else ProofLib.RAPIDSNARK
val isValid = verifyCircomProof(file.absolutePath, convertCircomProofResult(proofResult), proofLib)
isValid
} catch (e: Exception) {
throw CodedException("VerifyProofFailed", "Unknown error occurred during proof verification", e)
}
}
// ...
}
4. Define typescript APIs
Please refer to react-native-app to see the latest update.
-
Define the types for the native module. Add the following types in the file:
/modules/mopro/index.ts// Define the G1 type
export type G1 = {
x: string;
y: string;
z: string;
};
// Define the G2 type
export type G2 = {
x: string[];
y: string[];
z: string[];
};
// Define the CircomProof type
export type CircomProof = {
a: G1;
b: G2;
c: G1;
protocol: string;
curve: string;
};
// Define the CircomProofResult type
export type CircomProofResult = {
proof: CircomProof;
inputs: string[];
};
export enum ProofLibOption {
Arkworks,
Rapidsnark,
}
export type CircomProofLib = {
proofLib: ProofLibOption;
}; -
Add the native module's API functions in the same file.
/modules/mopro/index.tsexport async function generateCircomProof(
zkeyPath: string,
circuitInputs: string,
proofLib: CircomProofLib
): Promise<CircomProofResult> {
return await MoproModule.generateCircomProof(
zkeyPath,
circuitInputs,
proofLib
);
}
5. Run the app
5.1 Install expo-asset
Install expo-asset to use assets.
npx expo install expo-asset
5.2 Check the expo command
The android and ios scripts should be defined as follows to support running with the mobile native modules:
{
...
"scripts": {
...
"android": "expo run:android",
"ios": "expo run:ios",
...
}
...
}
5.3 Generate proofs in the app
Here is an example demonstrating how to generate a proof within an app:
import {
generateCircomProof,
verifyCircomProof,
ProofLibOption,
CircomProofLib,
CircomProofResult,
} from "@/modules/mopro";
const circuitInputs = {
a: ["3"],
b: ["5"],
};
const proofLib: CircomProofLib = {
proofLib: ProofLibOption.Arkworks,
};
const result: CircomProofResult = await generateCircomProof(
zkeyPath.replace("file://", ""),
JSON.stringify(circuitInputs),
proofLib
);
const valid: boolean = await verifyCircomProof(
zkeyPath.replace("file://", ""),
result,
proofLib
);
Please refer to react-native-app to see the latest update.
5.4 Run in simulators
-
Android
Export
ANDROID_HOMEexport ANDROID_HOME="~/Library/Android/sdk"Then run
npm run android -
iOS
npm run ios
6. What's next
-
Update your ZK circuits as needed. After making changes, be sure to run:
mopro build
mopro updatewarningThis ensures the bindings are regenerated and reflect your latest updates.
-
Build your mobile app frontend according to your business logic and user flow.
-
Expose additional Rust functionality: If a function is missing in Swift, Kotlin, React Native, or Flutter, you can:
- Add the required Rust crate in
Cargo.toml - Annotate your function with
#[uniffi::export](See the Rust setup guide for details).
Once exported, the function will be available across all supported platforms.
- Add the required Rust crate in